First you need to obtain a certificate from CA. This varies from provider to provider. I manage certificates using Server Certificates section in Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
On the right hand pane of Server Certificates you will see commands for importing or requesting the certificate. You can use them for internal or external CA’s.

If you need to create multi-name certificate (SAN or Subject Alternative Name) please use Exchange Management Shell:
New-ExchangeCertificate -GenerateRequest -KeySize 2048 -SubjectName "c=ee, s=Harjumaa, l=Tallinn, o=YourCompany, ou=IT, cn=mail.yourdomainname.com" -DomainName mail.yourdomainname.com, autodiscover.yourdomainname.com -PrivateKeyExportable $True -FriendlyName "mail.yourdomainname.com"
After equal signs (=) you should have: your country code, state, city, organization, OU and common name. Common name is the default name for the certificate (for example mail.yourdomainname.com). The domainname switch is for SAN names (alternative names, like autodiscover.yourdomain.com etc) separated by comma. SAN should include always the common name. FriendlyName is for identifying certificates (for example two certificates with same common name but different expiration date).
This command gives you the certificate request. You should copy and paste it into CA's web form to request a certificate. When you get back the certificate from CA, then you should complete the request by using Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
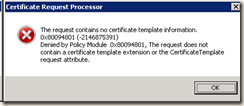
On Windows 2008 based CA you might get the error:
The request contains no certificate template information. 0x80094801 (-2146875391)
Denied by Policy Module 0x80094801,….
Then you will need to use command line to submit the request to CA:
certreq -submit -attrib "CertificateTemplate: WebServer" WebServerCertReq.txt
where the file name in the end of command line contains the output of New-ExchangeCertificate command.
OK. Let’s assume, you managed to create a new certificate.
To list all installed certificates, use Exchange Management Shell:
get-exchangecertificate | ft thumbprint,servicesstringform,friendlyname -a

Remember the thumbprint of your new certificate and enter following 4 commands to assign those certificates to 4 protocols (IMAP, POP, SMTP and HTTP).
Enable-ExchangeCertificate thumbprint -Services imap
Enable-ExchangeCertificate thumbprint -Services pop
Enable-ExchangeCertificate thumbprint -Services smtp
Enable-ExchangeCertificate thumbprint -Services iis
Replace the string “thumbprint” with the actual thumbprint from previous get-exchangecertificate command.
Restart POP and IMAP services and do a IISRESET using following commands in powershell as administrator:
get-service *pop3,*imap4 | restart-service
iisreset

If you have CAS array, you should do almost the same procedure on other CAS array members, with the exception, that you don’t need to request new certificate. You must export the existing certificate from first CAS member and import it to other servers.















