If you have IMAP clients, then you want to make sure that the connection is encrypted. By default IMAP uses TCP port 143 and SMTP for sending uses TCP port 25. For encrypted traffic the usual port assignments are TCP port 993 for IMAPS and 587 for SMTPS.
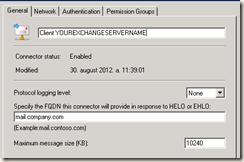
To make the access to Exchange via IMAP clients easier you probably use a nice common name like mail.company.com. For that name you have a 3rd party certificate (or a certificate from a local CA). This certificate must be installed on a local store on every Client Access Server. This can be done via IIS configuration window:
Just select the server name from the left and double-click Server Certificates icon. From there you can request or import a certificate:
If you have Active Directory Certificate Services, you can use Create Domain Certificate.
For enabling this certificate for different services you need to use Enable-Exchangecertificate cmdlet. To see available certificates for Exchange to use, use Get-Exchangecertificate cmdlet.
Enable-ExchangeCertificate uniqueid -Services popEnable-ExchangeCertificate uniqueid -Services smtp
Enable-ExchangeCertificate uniqueid -Services imap
Enable-ExchangeCertificate uniqueid -Services http
Uniqueid is the thumbprint that can be seen in Get-Exchangecertificate output.
For POP and IMAP to get working with new certificate, you must restart corresponding services. For SMTP to get working, you must change the FQDN on affecting receive connector:
The FQDN must be the same as the common name on the certificate.